Both pterygoids protract the mandible and move it from side to side during chewing. Using the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles as references identify the buccal branch of the mandibular nerve CN V3 and accompanying buccal artery.

Medial Pterygoid Learn Muscles
Medial pterygoid muscle consists of two heads.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14110/Pterygoid_muscles.png)
. The pterygoids are often weak and inactive due to the underdevelopment of the maxilla which causes occlusion to establish too posteriorlyThe pterygoids pro. Its fibers pass downward lateral and posterior and are inserted by a strong tendinous. Medial pterygoid is a thick quadrilateral muscle that connects the mandible with maxilla sphenoid and palatine bones.
Protrusion elevation medial movement of mandible. The nerve and artery usually pass between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle. These movements maximize the efficiency of the teeth while chewing or grinding foods of various consistencies.
Lateral pterygoid TrPs Refer often severe pain into the maxillary sinus deeply into the TM joint produce dysfunctions of the joint. The medial pterygoid can be very hyperactive in jaw closing dystonia as a result of the so-called whack-a-mole phenomenon after repeated botulinum toxin injections into the masseter and temporalis muscles. Lateral pterygoid medial pterygoid.
Ultrasound Guided Injection for Medial and Lateral Pterygoid Muscles. Using the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles as references identify the buccal branch of the mandibular nerve CN V3 and accompanying buccal artery. These two nerves pass between the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles.
The medial pterygoid muscle causes pain in the temporomandibular joint and the ear which increases when you bite down on something. Protrusion depression medial movement of mandible. The Living Units 4 Tissue.
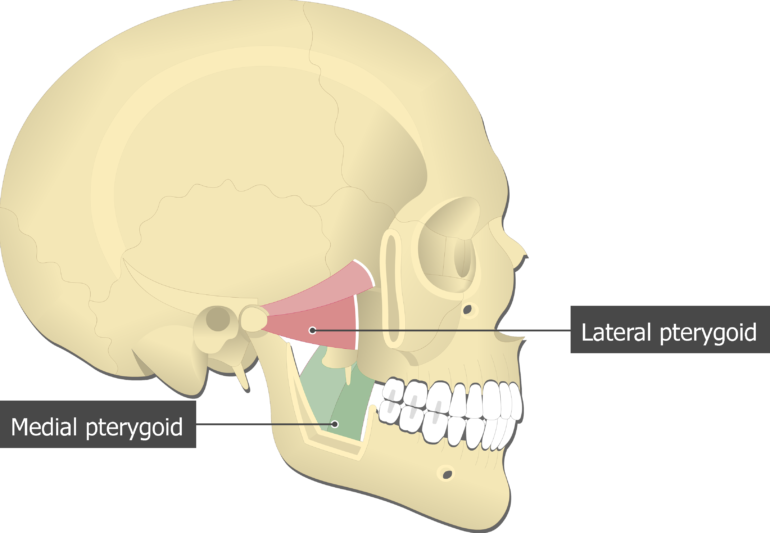
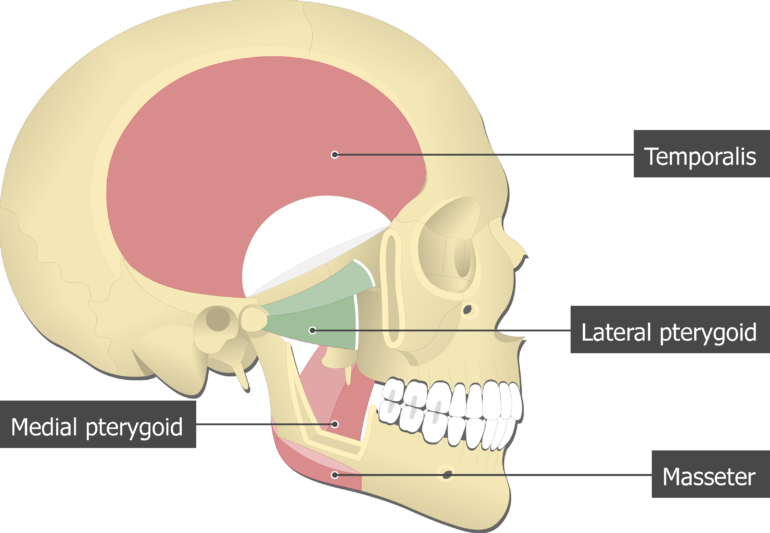
It can assist in protrusion of the mandible. Masseter lateral pterygoid superior and inferior bellies. Medial and Lateral Pterygoids are both well hidden by the lower jaw bone.
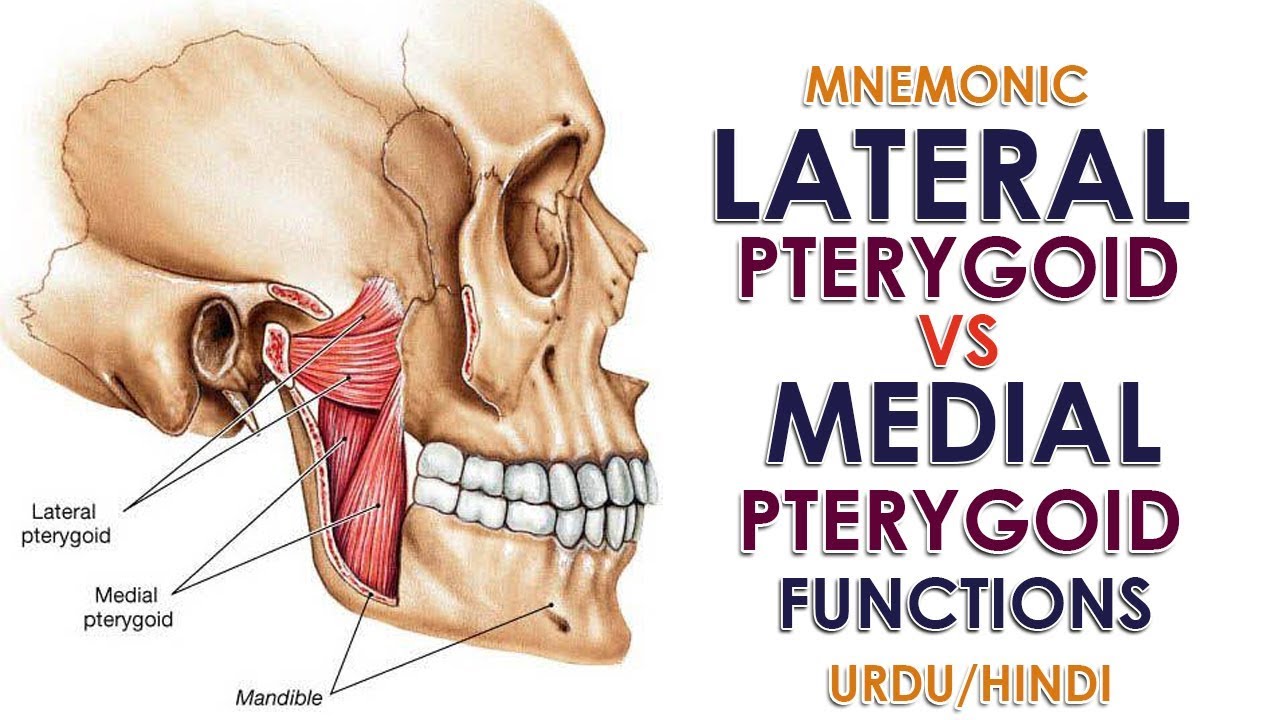
The medial pterygoid also elevates the mandible. The medial pterygoid muscle causes pain in the temporomandibular joint and the ear which increases when you bite down on something. The medial pterygoids temporalis and masseter muscles elevate the mandible to close the jaw and the lateral pterygoids help open it other muscles involved in jaw opening are the digastric and geniohyoid muscles.
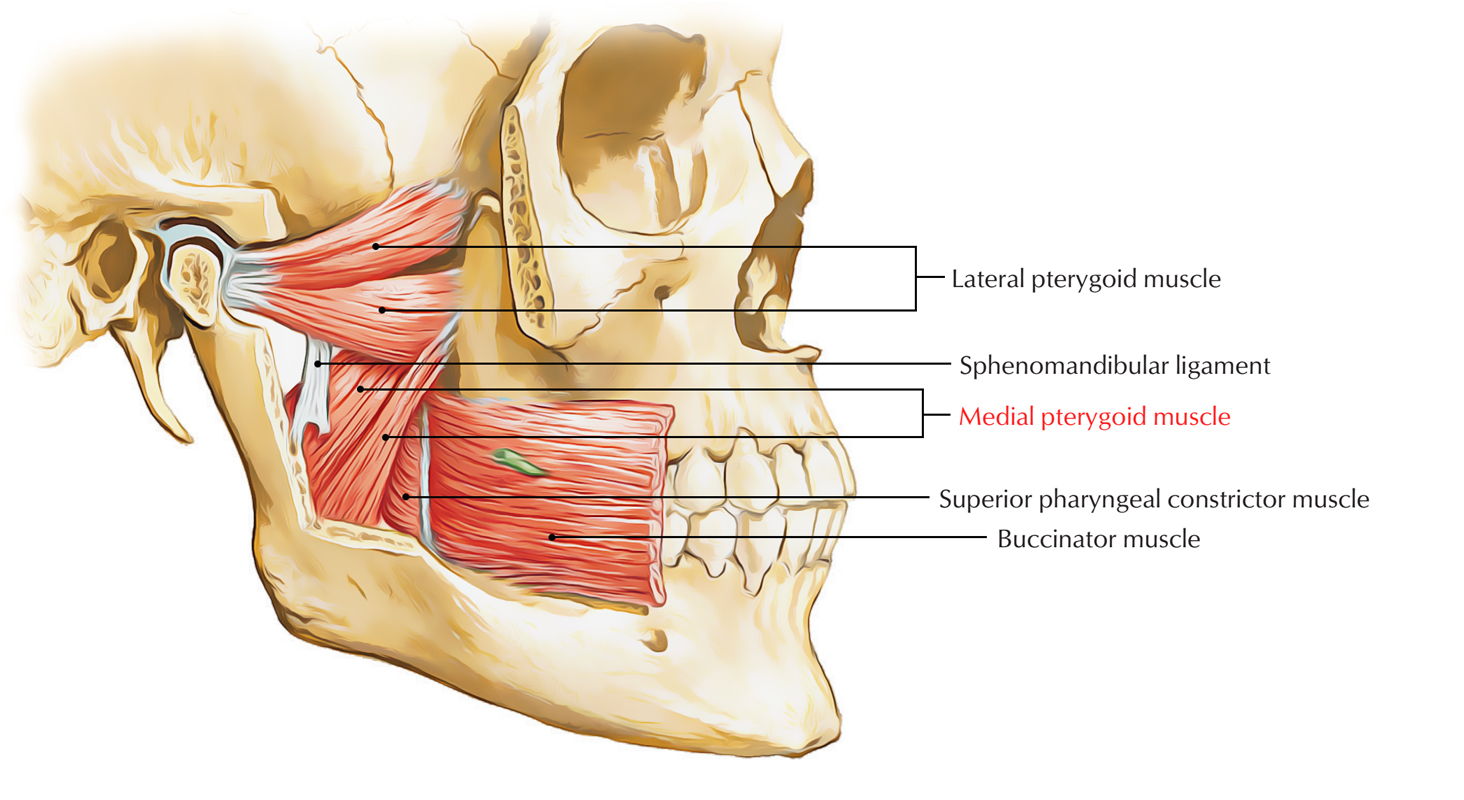
The deep head of the muscle originates from the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone. These two nerves pass between the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles. Pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery.
In general the pain caused by this muscle is rather diffuse and not clearly distinguishable. Medial and Lateral Pterygoids are both well hidden by the lower jaw bone. Tightness in this muscle can make it difficult to open the mouth wide.
The bulk of the muscle arises as a deep head from just above the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plateThe smaller superficial head originates from the maxillary tuberosity and the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. Slightly reduced range of opening deviations of mandible with opening altered occlusion my teeth dont fit together right tinnitus are common complaints associated with TrPs in this muscle. It belongs to the group of masticatory muscles along with the lateral pterygoid masseter and temporal muscles.
The medial pterygoid muscle has a superficial and a deep head which arise from different areas of the jaw. Lateral Pterygoid this muscle lives directly behind your upper back molar using the same-sided hand ie right hand for right pterygoid with your palm against your cheek place your pinky inside your cheek on the row of upper teeth your jaw can rest closed once. Tightness in this muscle can make it difficult to open the mouth wide.
The lateral pterygoids activate at an angle to one another and push the mandible forward. Medial pterygoid muscles arise from the lateral pterygoid plates of the sphenoid bone and insert on the mandible. The medial pterygoid muscle is a thick and square shaped muscle.
The Living Fabric 5 The Integumentary System 6 Bones And Skeletal Tissues 7 The Skeleton 8 Joints 9 Muscles And Muscle Tissue 10 The Muscular. Side-to-side movement which includes a rotational movement of the mandibular condyle on the side the movement is moving toward as well as gliding condylar motion upon the alternate side. The nerve and artery usually pass between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle.
Medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate and palatine bone. 1 The Human Body. A Novel Treatment for Orofacial Pain Med Ultrason.
The lateral pterygoid muscle via its lower head separates the two distinct heads. The medial pterygoid muscle attaches to the angle of the mandible and to the lateral pterygoid plate to form a sling with the masseter muscle that suspends the mandible Figure 6-19. Trigger points in the medial pterygoid can lead to the following ailments.
On the medial side deep surface the muscle is related to the mandibular nerve the middle meningeal artery the sphenomandibular ligament and the upper part of the medial pterygoid muscle. Although having different origins both heads insert on the inner. Click to see full answer.
The medial pterygoid muscle consists of two heads. The superficial head of the medial pterygoid muscle originates from the maxillary tuberosity of the maxilla and pyramidal process of the palatine bone. Elevation of the mandible protraction of the mandible when medial and lateral pterygoid muscles contract bilaterally displacement of the mandible to the contralateral side when the just the ipsilateral medial and lateral pterygoid muscles contract It has a key role in mastication.
Authors Yunn Jy Chen 1 Pei-Hsuan Chang 2 Ke-Vin Chang 3 Wei-Ting Wu 4 Levent Özçakar 5 Affiliations 1 Department of Dentistry School of. Platysma medial pterygoid Laterotrusionlateral deviation. The smaller superficial head has its origin mainly from the maxillary tuberosity with some fibers arising from the pyramidal process of the palatine bone.
The primary action is to elevate the mandible and laterally deviate it to the opposite side. On the lateral side superficial surface the lateral pterygoid muscle relates to the mandibular ramus maxillary artery temporalis tendon and the masseter muscle. An Orientation 2 Chemistry Comes Alive 3 Cells.
The pain usually increases when you stretch or contract the muscle. Attachments of Medial Pterygoid Muscle. Jaw opening jaw deviation and jaw protrusion types of oromamdibular dystonia are caused by involuntary contraction of the lateral pterygoid muscles.
Pain under and behind the temporomandibular joint. The superficial head is attached to the maxillary tuberosity and the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. Branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve CN V3 Blood supply.
Medial pterygoid is a thick quadrilateral muscle that connects the mandible with maxilla sphenoid and palatine bones. Medial surface of ramus and angle of mandible. It has two heads of origin.
It belongs to the group of masticatory muscles along with the lateral pterygoid masseter and temporal muscles. Click to see full answer. The deep head is the major component and is attached to the medial aspect of the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone.
Medial pterygoid has several actions. Medial pterygoid muscle consists of two heads.

Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Wikipedia
Medial Pterygoid Muscle Earth S Lab
Medial Pterygoid Muscle Attachments Actions Innervation
Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Attachments Actions Innervation
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14110/Pterygoid_muscles.png)
Medial And Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Anatomy And Function Kenhub
Mnemonic Lateral Pterygoid Vs Medial Pterygoid Function Urdu Hindi Youtube
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14112/IjxD1w7xmfmSR4xC7FugCQ_Pterygoideus_lateralis_02.png)
Medial And Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Anatomy And Function Kenhub

0 comments
Post a Comment